So, an absolute value of any number is positive. For example, an absolute value of -5 is 5.
The absolute value of \(x\) is denoted as \(|x|\).
Example What is \(|-3|\) and \(|3|\)?
Solution \( \enspace |-3|=|3|=3 \)
Special Case
In the case where \(\sqrt{x^2}\), \(x^2\) is always greater than 0 so \(\sqrt{x^2}\) is the same as \(|x|\).\(\enspace \sqrt{x^2}=|x|\)
Number Line
GMAT questions frequently use number lines when involving absolute values. You need to get familiar with number lines.On a number line, \(|x| \leq 2\) is denoted as
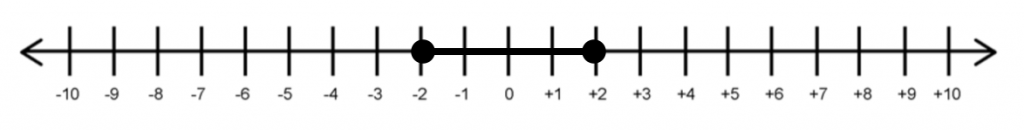
\(|x| \geq 2\) is denoted as
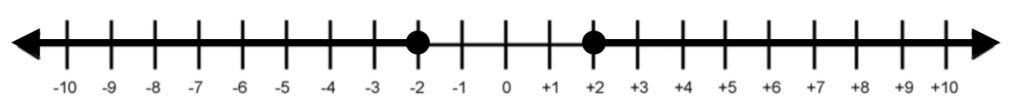
For absolute values wihtout any equal(=) signs, the dots on the number lines are denoted as white dots.
\(|x| < 2\) is denoted as
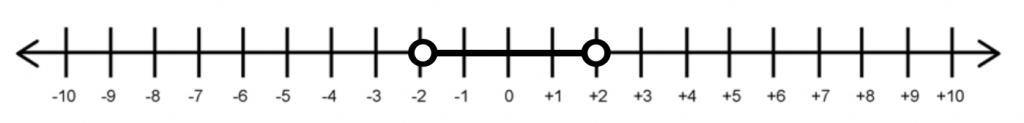
\(|x| > 2\) is denoted as
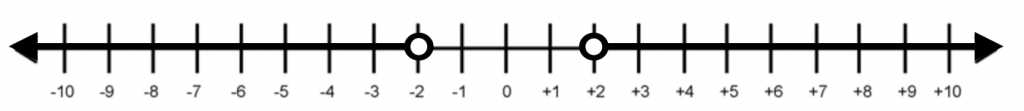
So black dots indicate that the value is inclusive, while the white dots indicate the value is exclusive.
Example What is \(|-3x|\) if \(x=2\)?
Solution \( \enspace |-3x|=|-3(2)|=|-6|=6 \)
Example Denote the following number line in terms of absolute values and inequalities.
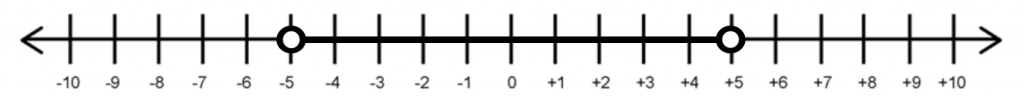
Solution \( \enspace |x| < 5 \)
Example Write \(\sqrt{7^2}\) in terms of absolute values.
Solution \( \enspace \sqrt{7^2}=|7| \)
What is \(|-7x|\) if \(x=3\)?
Write \(\sqrt{5^2}\) in terms of absolute values.
Denote the following number line in terms of absolute values and inequalities.
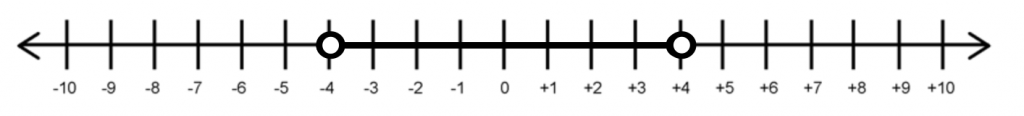
Write \(\sqrt{5^2}\) in terms of absolute values.
Denote the following number line in terms of absolute values and inequalities.
